
Word Structure
Many morphemes are very helpful for analysing unfamiliar words. Morphemes can be divided into prefixes, suffixes, and roots/bases.
Roots/Base words
Roots provide the main meaning of a word and can be connected to other roots, prefixes, and suffixes.
Prefixes
Prefixes come before root words and act as modifiers.
Suffixes
Suffixes come after the root word and act as modifiers.

General Processes
Derivation
Derivation processes form new words (generally of a different category) from existing words, in English this is mainly done by adding affixes. For example, industrialization, and destruction can be thought of as being derived in the way illustrated below.
Compounding
In grammar, compounding, also called composition, is when two or more words are combined together to form a new word. For example, the word underground is a combination of the words under and ground.
Parasynthesis
The formation of words by a combination of compounding and adding an affix, as in brown-eyed. (grammar) The formation of words in which the prefixing and the suffixing are involved simultaneously, as in multifaceted.

Components
Morph
A morph is a phonological string (of phonemes) that cannot be broken down into smaller constituents that have a lexicogrammatical function. In some sense it corresponds to a word-form. An allomorph is a morph that has a unique set of grammatical or lexical features. All allomorphs with the same set of features forms a morpheme. A morpheme, then, is a set of allomorphs that have the same set of features.
Morpheme
Morphemes are comprised of two separate classes called (a) bases (or roots) and (b) affixes. A "base," or "root" is a morpheme in a word that gives the word its principle meaning. An example of a "free base" morpheme is woman in the word womanly. An example of a "bound base" morpheme is -sent in the word dissent.

Content
Content words are usually nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. A noun tells us which object, a verb tells us about the action happening, or the state. Adjectives give us details about objects and people and adverbs tell us how, when or where something is done. Nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs give us important information required for understanding.

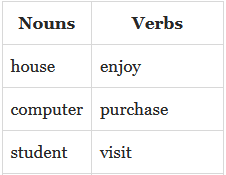
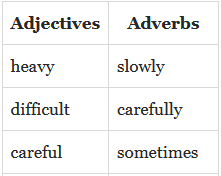

Function
Function words help us connect important information. Function words are important for understanding, but they add little meaning beyond defining the relationship between two words. Function words include auxiliary verbs, prepositions, articles, conjunctions, and pronouns. Auxiliary verbs are used to establish the tense, prepositions show relationships in time and space, articles show us something that is specific or one of many, and pronouns refer to other nouns.



Affixation/Compounding
In affixation, a bound morpheme is affixed to a base. Compounding derives a new word by joining two morphemes that would each usually be free morphemes.
Clitization
An unstressed word, typically a function word, that is incapable of standing on its own and attaches in pronunciation to a stressed word, with which it forms a single accentual unit. Examples of clitics are the pronoun 'em in I see 'em and the definite article in French l'arme, "the arm."

Suppletion
Substitution
Suppletion is a form of morphological irregularity whereby a change in a grammatical category triggers a change in word form, with a different (suppletive) root substituting for the normal one (e.g. in the past tense of go, the irregular form went replaces the regular goed).
Substitution in English grammar is when a word, phrase, or clause in a sentence is replaced by a different word or phrase (e.g. one, do, this) in order to avoid repeating the previously used word.
Reduplication
In linguistics, reduplication is a morphological process in which the root or stem of a word or even the whole word is repeated exactly or with a slight change.

Conversion
Clipping
In linguistics, conversion, also called zero derivation or null derivation, is a kind of word formation involving the creation of a word from an existing word without any change in form, which is to say, derivation using only zero. For example, the noun green in golf is derived ultimately from the adjective green.
Stress and Tone
In linguistics, clipping, also called truncation or shortening, is word formation by removing some segments of an existing word to create a synonym. Clipping differs from abbreviation, which is based on a shortening of the written, rather than the spoken, form of an existing word or phrase.
Word stress is the emphasis we place in a specific syllable of a word when pronouncing it. In English words that have more than one syllable, we usually don't pronounce every syllable with the same weight, so each syllable in a word can be stressed or unstressed.

Backformation
In etymology, back-formation is the process or result of creating a new word via inflection, typically by removing or substituting actual or supposed affixes from a lexical item, in a way that expands the number of lexemes associated with the corresponding root word.
Blends
Blending is a type of word formation in which two or more words are merged into one so that the blended constituents are either clipped, or partially overlap. An example of a typical blend is brunch, in which the beginning of the word breakfast is joined with the ending of the word lunch.

Acronyms
acronym. A word formation process in which the first letters (sometimes the first few letters) of the words in a phrase are extracted and put together to form a word, pronounced as a word by the usual rules of English spelling, with the same meaning as the original phrase.
Onomatopoeia
An onomatopoeia is the forming of a word by imitating the sound the word is referring to, as in bang, meaning “a loud, explosive sound,” and meow, meaning “the sound a cat makes.” The words themselves are also known as onomatopoeias. Many commonly used words are onomatopoeias.

